The evolving standards behind nascent 5G technology mean that testing standards need end-to-end integration, argues this test solutions expert.
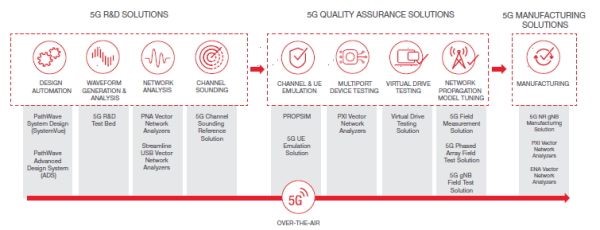
From research and development to quality assurance to manufacturing, 5G technology introduces disruptive changes for network equipment manufacturers and component manufacturers. With standards continuing to evolve, the 3rdGeneration Partnership Project (3GPP)’s Release 16 has added new capabilities to support cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), unlicensed bands, and high frequencies.
To support the technical complexity of a variety of 5G applications, network equipment manufacturers must integrate sophisticated multichannel antennas into 5G base stations, covering many frequency bands while reducing latency and adding support for a broad range of machine and user behavior.
Also, engineers must develop novel ways to implement the physical layer in communications systems. They must verify that their designs comply with the latest 5G standards and meet the expectations of enterprises and consumers.
Achieving conformance with 5G standards requires thorough functional and performance testing spanning radio access network (RAN) and core aspects. It also requires testing with real-world conditions.
Meanwhile, in manufacturing, network equipment and component manufacturers must juggle the competing priorities of accelerating time to market while reducing the cost of test. This in itself is nothing new, but the increased complexity of 5G makes it more challenging.
Network equipment manufacturers require innovative test strategies to ensure a smooth transition from Quality Assurance all the way through to volume manufacturing. Addressing all of 5G’s many test challenges—including the inclusion of millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies and over-the-air (OTA) testing—is critical.
Component manufacturers, meanwhile, need supreme confidence in the integrity of their measurements.
Adopting the right test solution
The only way for network equipment and component manufacturers to grapple with all of the new requirements and technical challenges imposed by 5G is to adopt design and test solutions that span the entire workflow, including design automation, development, and design verification, as well as conformance and manufacturing test.
Part of adopting effective end-to-end testing is to modify manufacturing tests to leverage work done, and data gathered, at each stage of the design-to-manufacturing workflow.
Optimizing the transition from conformance tests to manufacturing is the critical ingredient for network equipment and component manufacturers to hit tight market windows and ensure profitability.
Using the same measurement algorithms across the workflow helps reduce development time by giving engineers higher confidence in their measurement results. Traceability back to design accelerates resolution when issues occur. Adopting common test platform elements is essential for moving network equipment through the workflow quickly. Using common test platform elements also helps with controlling the cost of test for globalized operations.
Component manufacturers have traditionally used different platforms across the workflow, from R&D to design validation to manufacturing. They have also traditionally relied on different form factors in each phase of the workflow. Transitioning to a common user interface across platforms helps minimize learning time.
For network analysis, key performance metrics, including dynamic range, measurement speed, trace noise, and temperature stability, matter above all others. These specifications enable component manufacturers to measure their devices more accurately or faster. Leveraging hardware across form factors yields similar levels of performance on key specifications by enabling component manufacturers to achieve consistent measurement results.
