Analyses of search engine metrics of AI tool websites for the period Sep 2022 to Aug 2023 has revealed interesting trends.
With generative AI chatbot ChatGPT opening up a can of worms, the popularity of GenAI and related tools has been the talk of the town in 2023.
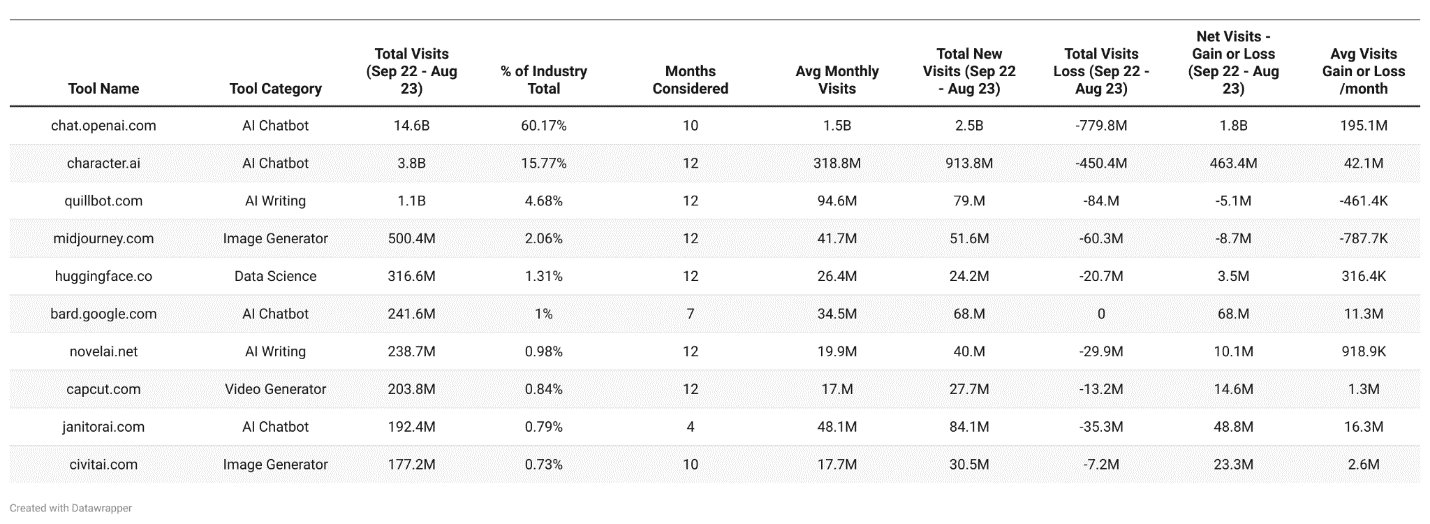
So, which AI tools and trends are worthy of our readers’ attention and exploration? According to research by Writerbuddy.ai, in the period ranging from Sep 2022 to Aug 2023, out of over 3,000 AI tools available worldwide, the following 50 attracted the most attention, with 24bn visits.
ChatGPT led with 14bn visits, comprising over 60% of the traffic analyzed. AI chatbot tools were the most popular, garnering 19.1bn visits overall. Out of the 50 AI tools receiving the most attention (for various reasons), the top 10 listed in the research were:
The websites gaining the top increases in traffic were:
- chat.openai.com
- character.ai
- bard.google.com
- janitorai.com
- perplexity.ai
- civitai.com
- leonardo.ai
- elevenlabs.io
- capcut.com
- cutout.pro
Noting the some tools such as Craiyon, MidJourney, and Quillbot faced the largest traffic declines during the analysis, researchers have offered the following possible causes based on their chronology:
- Regulatory changes: Stringent government regulations and related causes could have affected how AI firms operate, potentially impacting corporate strategies and user engagement levels.
- Economic burnout: The hype around many of the tools could have started wearing thin. While the interest overall was still huge (around 10.7x that of the previous year), the period of hype where everyone was just checking out the tools, may have been reduced.
- Shifts in consumer preferences: Trends and public opinion can change rapidly, and a shift in user trust or interest due to ethical concerns or a preference for non-AI solutions could have impacted traffic.
- AI firms may have developed mobile apps, leading users to access services directly on their phones instead of through web browsers. This shift could have caused web traffic to decline even if overall user engagement remained high or up-trending, as activity moved from traditional websites to mobile platforms.
