No, their onboard supercomputers will not help you fight villains and drive underwater to evade attack, but …
… Imagine a world where your car can be used to help with your day-to-day schedule.
Its electronics observes your work calendar, detects that you have a meeting scheduled for 8:00 am and checks the traffic situation for the best route to the office, just to make sure you will not be held up in any traffic jam.
As Big Data in the Cloud crunches information to derive the ideal time that you should leave your home by, the smart car can send a prompt to your phone or smartwatch to remind you of your meeting, acting as your virtual car valet service!
If you do not think this is possible, note that times have changed. The automotive industry can no longer disregard the significance of the Internet of Things. From connected cars to smart transportation systems, IoT is helping the automotive industry build next-generation connected vehicles.
The tech is already here
The combination of a wide variety of advanced technologies is paving the way for the connected car ecosystem.
- Sensors, including optical sensors, radio detection and ranging (RADAR), light detection and ranging (LIDAR)
- Information systems that integrate automotive ethernet networking, powerful signal processing, high definition mapping with high precision navigation, and AI
- Communication for vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-network (V2N), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P), vehicle-to-utility (V2U), and eventually, vehicle-to-everything (V2X)
When technologies like 5G wireless connectivity and the IoT are combined, we can develop new capabilities and applications to propel the automotive industry forward, exploiting enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
The acronyms may sound overwhelming, so let us break down each of these features to see how it can meet the needs and wants of the future connected car.
- 5G will be super fast with eMBB. With 5G reaching 10 Gigabits per second, it is up to 100 times faster than 4G networks. It will be able to support richer media data and interactivity with 3D videos and augmented reality/virtual reality.
- Communications will be almost instantaneous with URLLC. There will be a very little delay—1 to 5 milliseconds on a 5G network— as opposed to 20 milliseconds via current 4G networks. For autonomous vehicles, it will mean an almost real-time latency, providing users with safety information even before it is visible to the driver.
- Connect a great number of devices reliably with the mMTC feature. A large number of cars will be able to exchange information that can be used for traffic control or to warn drivers of dangers.
Five hypes you may look forward to
Here are the five ways the technologies can transform your driving experience some day:
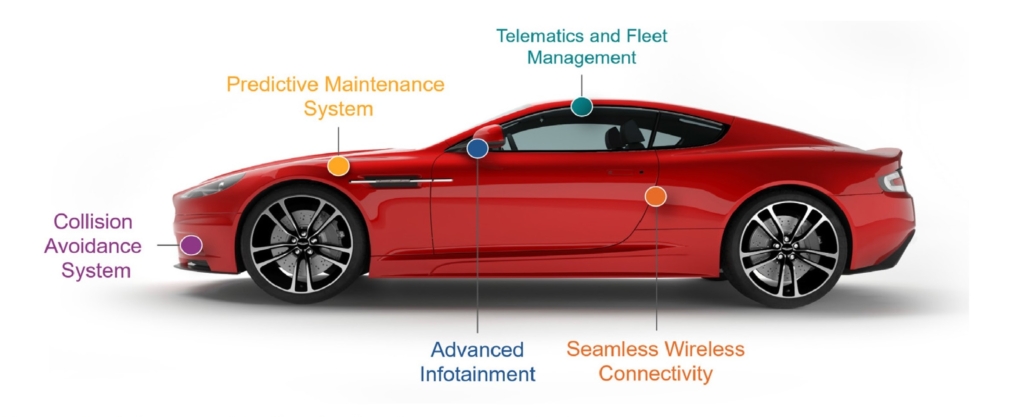
- Predictive maintenance
Through its various connected sensors, the vehicle can identify potential or imminent issues before they happen in the battery, fuel pump and starter motor. Combining this data using AI and additional general vehicle data stored in the Cloud will predict potential maintenance issues that may be difficult to diagnose using regular data from previous repairs. Mechanics will use predictive data analytics to deliver recommendations to the drivers via the vehicle or a connected device. V2C communications will enable over-the-air software updates and remote diagnostics. Drivers can take proactive steps in maintaining the vehicle to avoid possible failure while driving. - Advanced infotainment
The infotainment system is a collection of systems that deliver entertainment and vehicle data to the drivers and passengers for a safe and comfortable drive. It will interact with other in-vehicle and external systems such as an integrated head unit, connectivity modules, and integrated automotive sensors. Manufacturers are integrating AI, AR, and VR capabilities for a more immersive in-vehicle infotainment featuring audio-visual experiences and virtual reality. - Telematics and fleet management
Automotive telematics systems can track real-time details of the vehicle like speed and idling, fuel usage, tire pressure, vehicle status, and more. In situations where temperature-controlled transport is important, the data can help fleet managers optimize travel routes, reduce operational expenses, increase fleet security and driver safety, and manage remote maintenance. Temperature monitoring with cargo sensors will maintain the correct temperature for perishable foods. - Traffic safety service
Real-time information sharing on traffic and road conditions among road users and pedestrians can be achieved via the data collected from the national 5G-based infrastructure, 5G communication devices embedded in cars, and smart devices from pedestrians sent to the Cloud. Applications and systems that analyze the real-time data will warn drivers about hazardous road conditions and traffic congestion in real-time. - Improving environmental sustainability
Data collected from vehicles, pedestrians, and infrastructures can reveal a great deal about the city. Governments can use this data to create a greener environment: IoT-connected streetlights that will only turn on if pedestrians are detected in the vicinity; or traffic lights that autonomously divert traffic when there is traffic congestion, to reduce unnecessary carbon emissions. This will help the city save on electricity consumption.
Automotive industry as a tech showcase
The modern automobile is becoming a sensor-loaded IoT device showcase. Advanced communication systems, onboard computing power, and cloud-based data storage have created the foundation for a more efficient, safer, sustainable, and autonomous future.
Like any other IoT device, rigorous design and testing are paramount to ensure that all sensors are robust and resilient, complying with the 5Cs of device lifecycles: connectivity, continuity, compliance, co-existence, and cybersecurity.
